Hermes v0
The rocket of rebirth
Highlights
Overview
Hermes V0 is the first rocket of the test series Hermes. It is the first rocket completed after a while in Skyward and born as a low cost test platform for Rogallo wing and all subsystems developed for Rocksanne 2alpha. This project starts the rebirth of skyward and allows the new members to deal with a project from the beginning till the end. Hermes was completed in 6 month of work with a small team of 25-30 people and launched at a Roccaraso in May 2019 resulting in ballistic flight due to an expulsion system failure
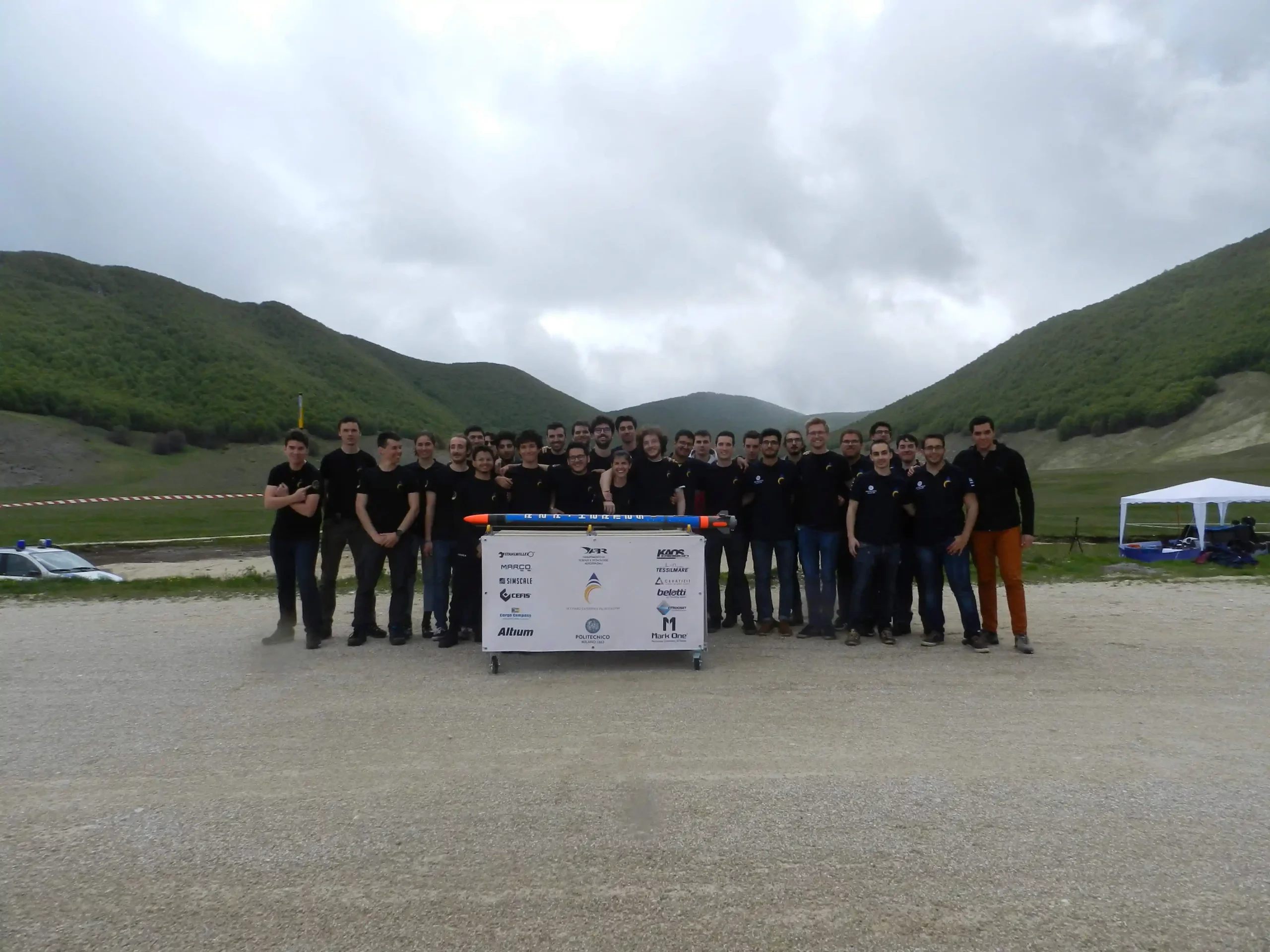


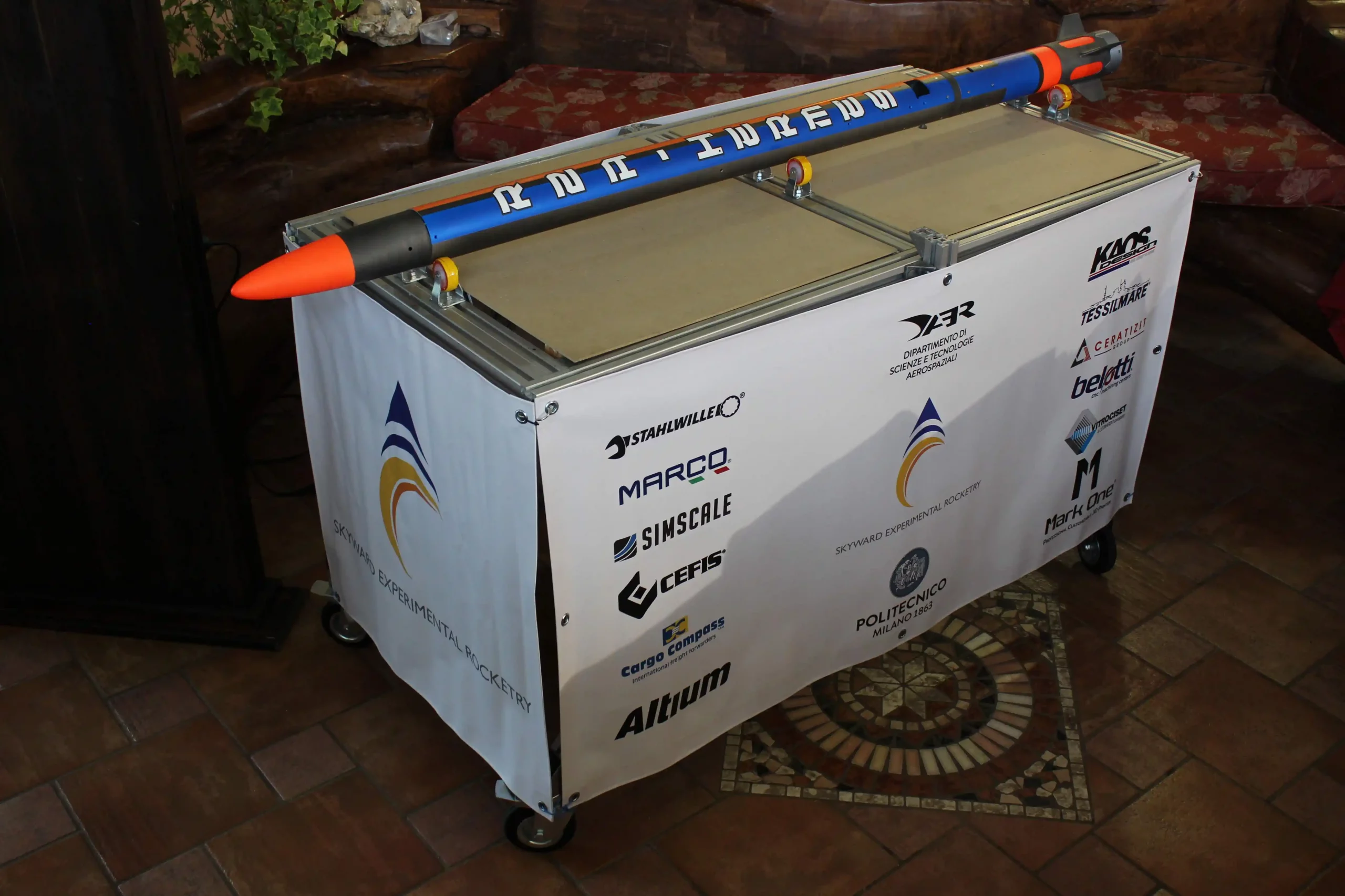
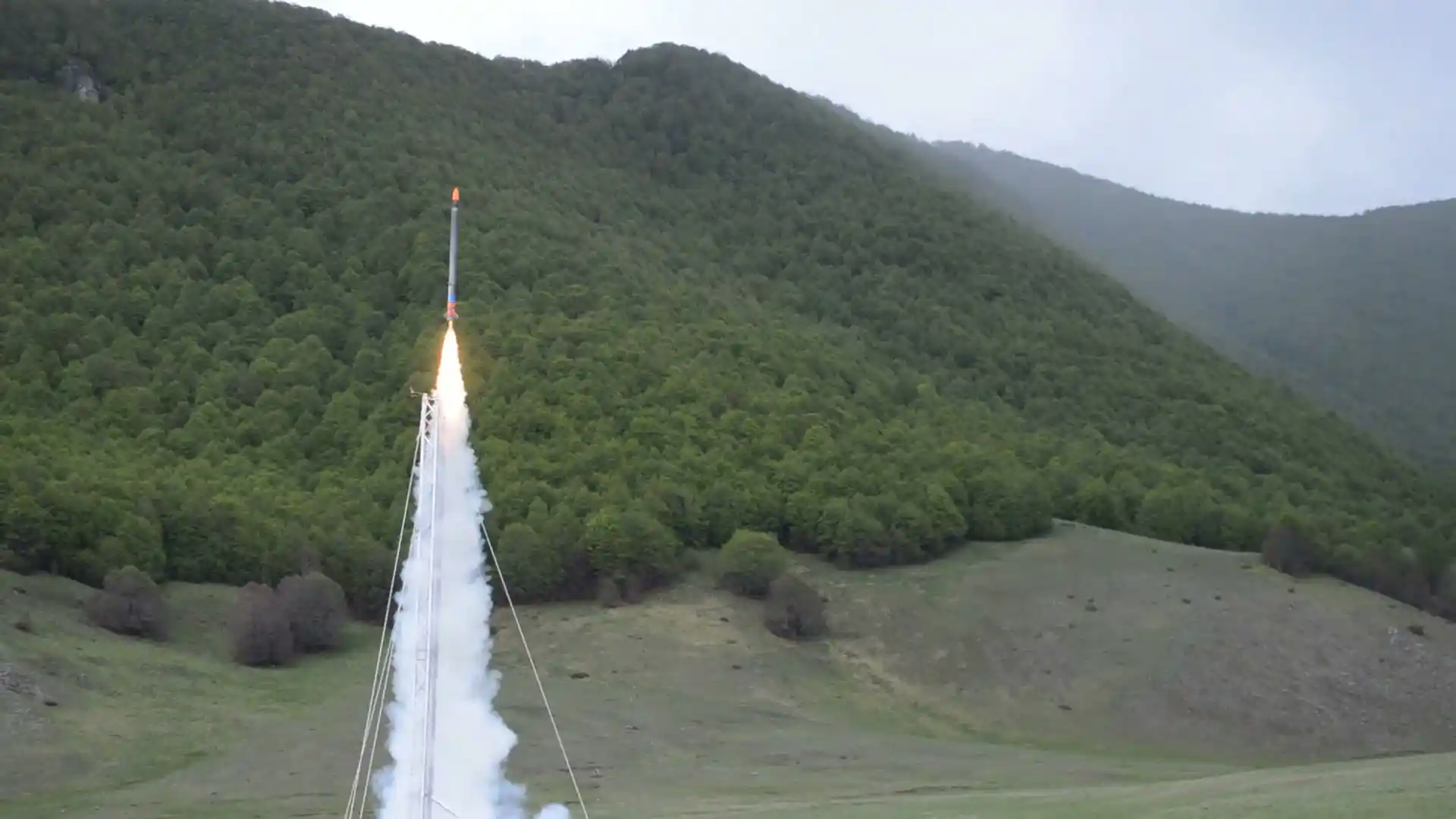
Roccaraso Flight
Hermes was launched on 28th of May at Piano dell’Aremonga at Roccaraso (AQ). It reached an apogee of 1118 m above the ground level and then for a failure of the expulsion system the nose cone didn’t open and the rocket went ballistic. The rocket was found 1 km on the side of the mountain in the middle of the forest thanks to GPS. This launch set the Italian altitude record for a student rocket and the 4th launch in the history of skyward.


specs
Aerotech
K550



Structure
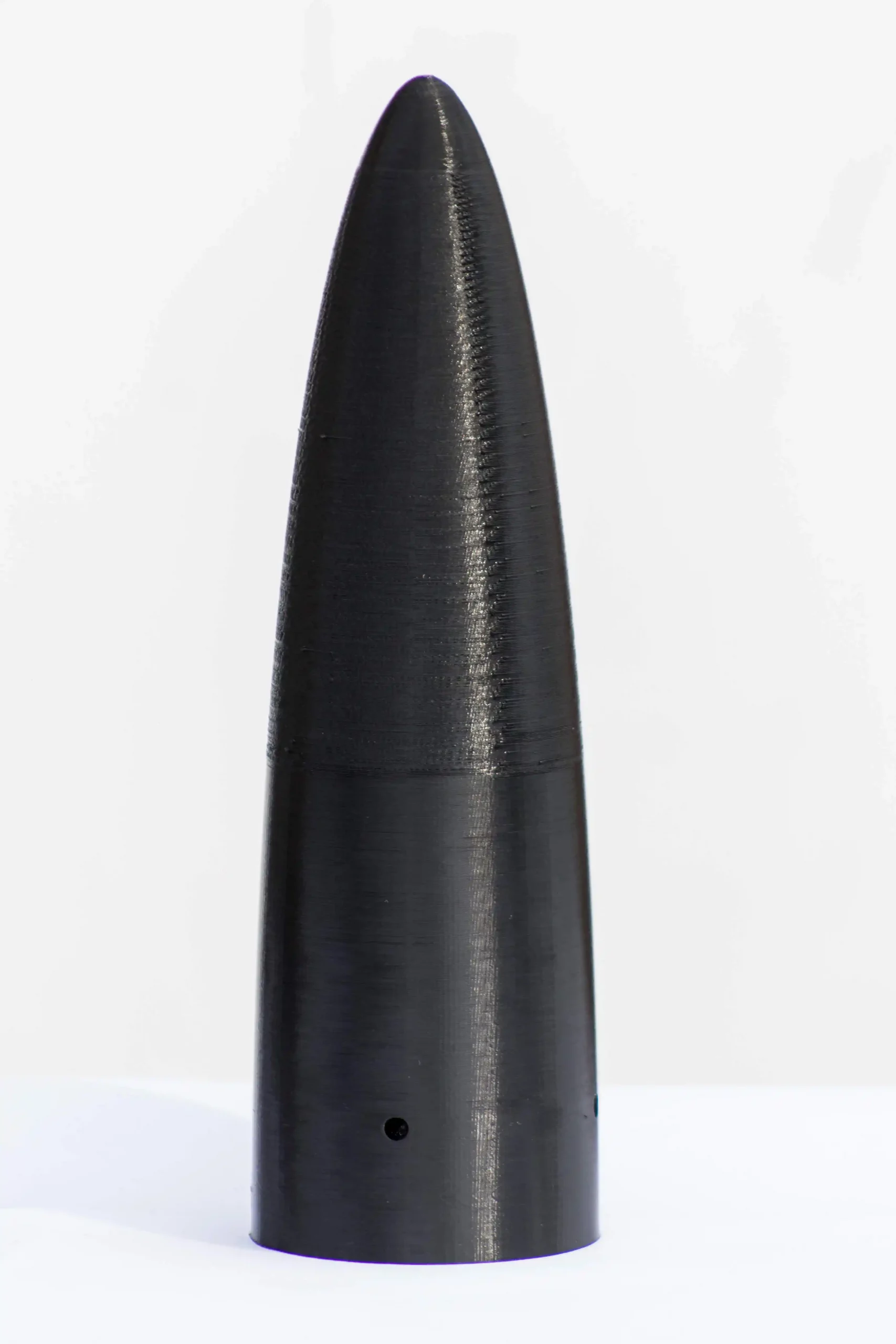
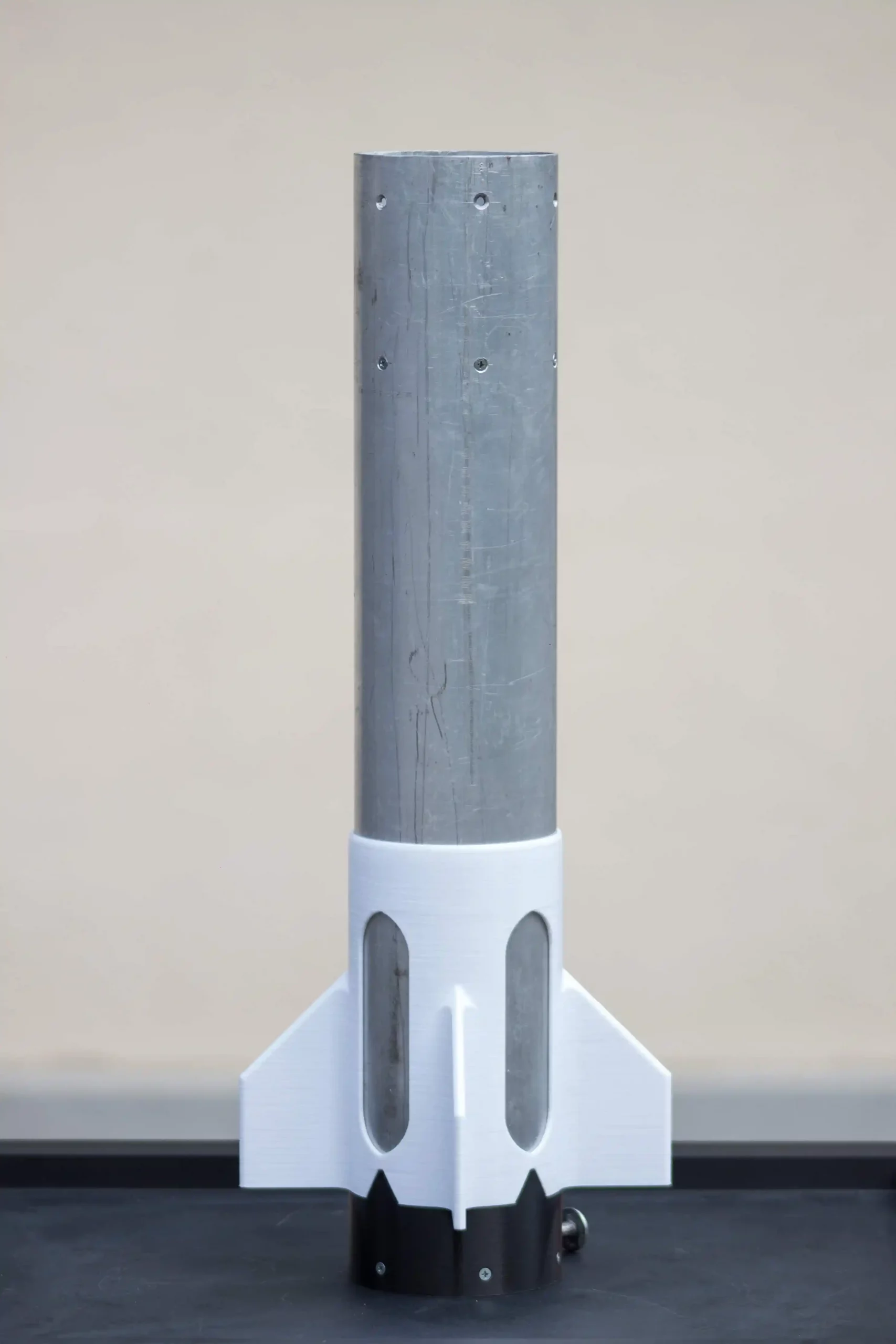
The Rocket is almost 2 m long with an external diameter of 9 cm. The fuselage is divided into 2 aluminum tubes with a thickness of 2 mm. The two parts are connected with an internal coupling tube: the lower one contains the solid COTS motor and holds the 3D printed PLA set of fins, instead the upper one contains all the electronics and the parachutes. The nose cone 3D printed in PLA contains the expulsion system also made in additive manufacturing, such as many other internal pieces of the rocket. With this new technology it is possible to use complex shapes and reduce the manufacturing process and cost.
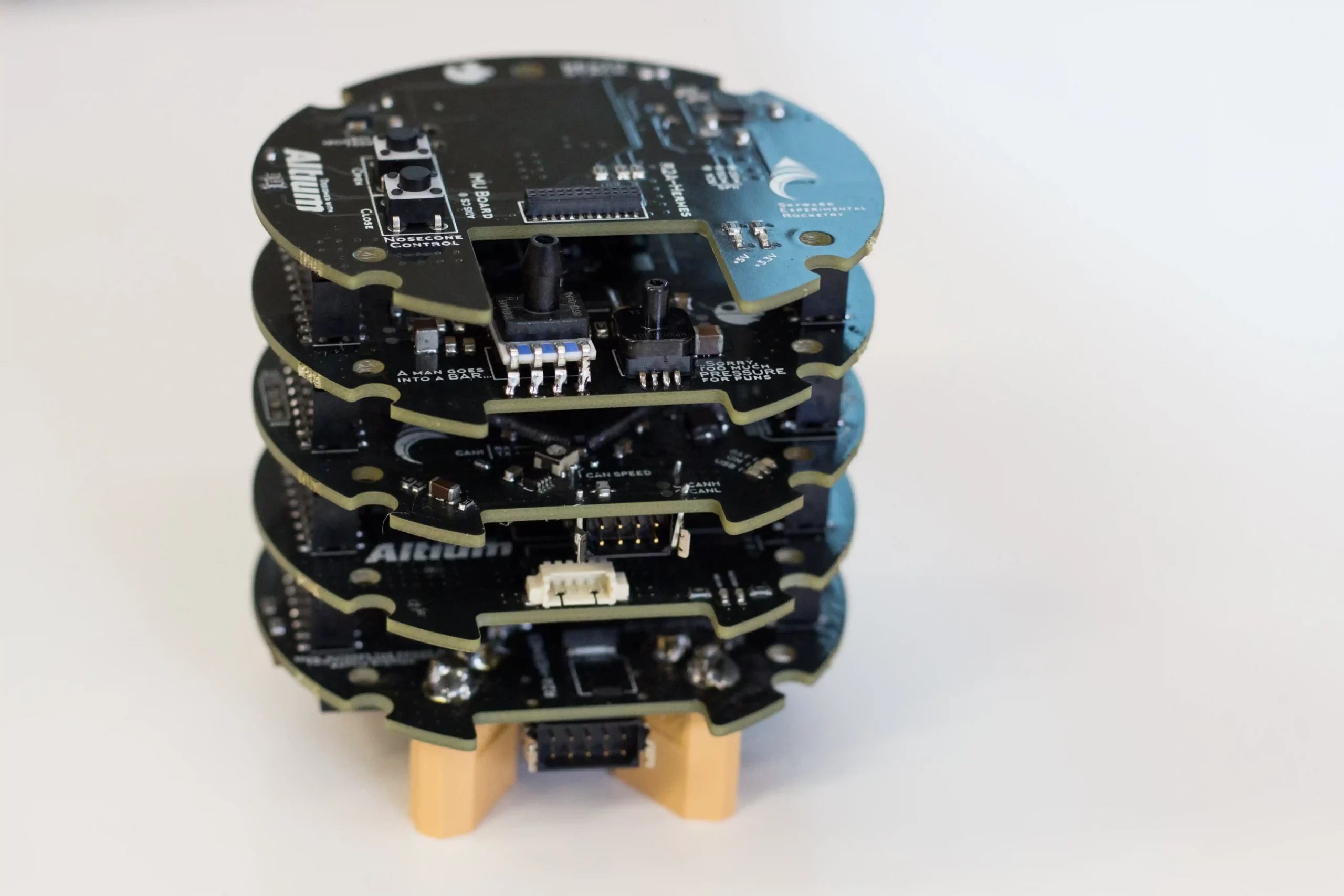
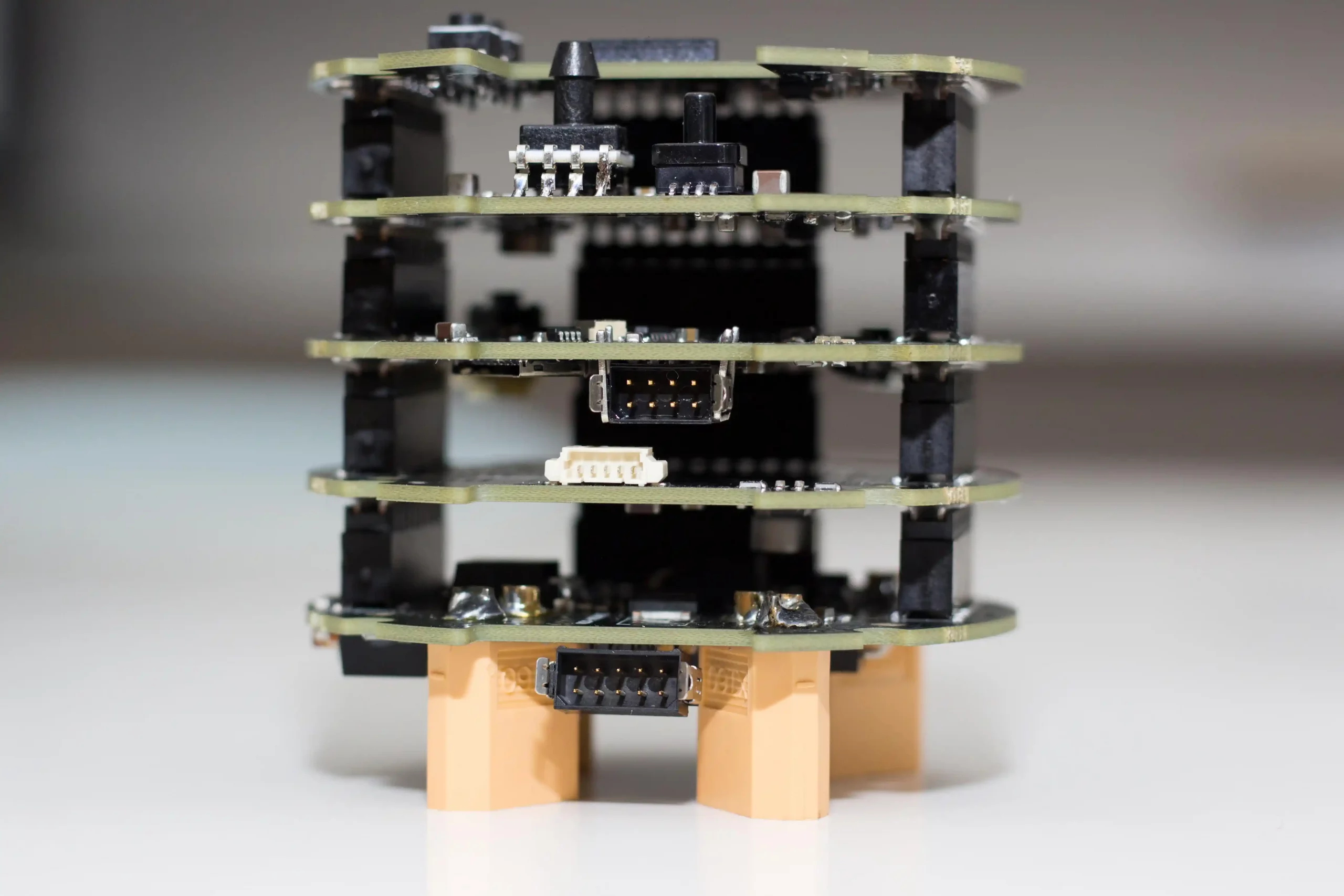
Electronics
The death stack V1 is the first modular flight computer of skyward built and designed by the electronics department. It presents a STM32 microcontroller, a power board to manage the power distribution from 12V LiPo and an analog board with several sensors to retrieve flight data. The main function of the stacks are:
- Record the telemetry data and store them on a SD card
- Detect the apogee using the ADA algorithm and send the command for nose cone opening
- Manage the telemetry link with ground

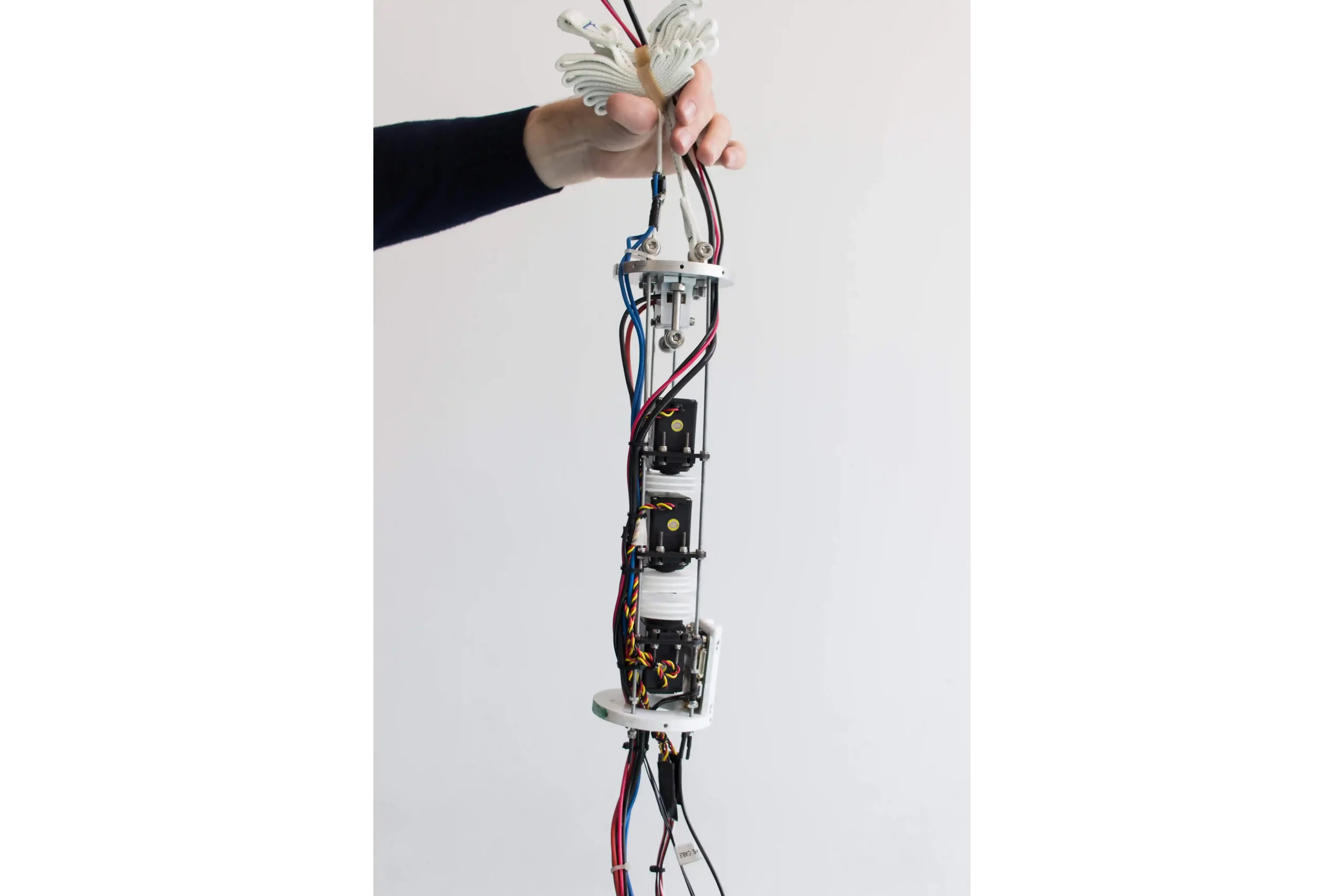
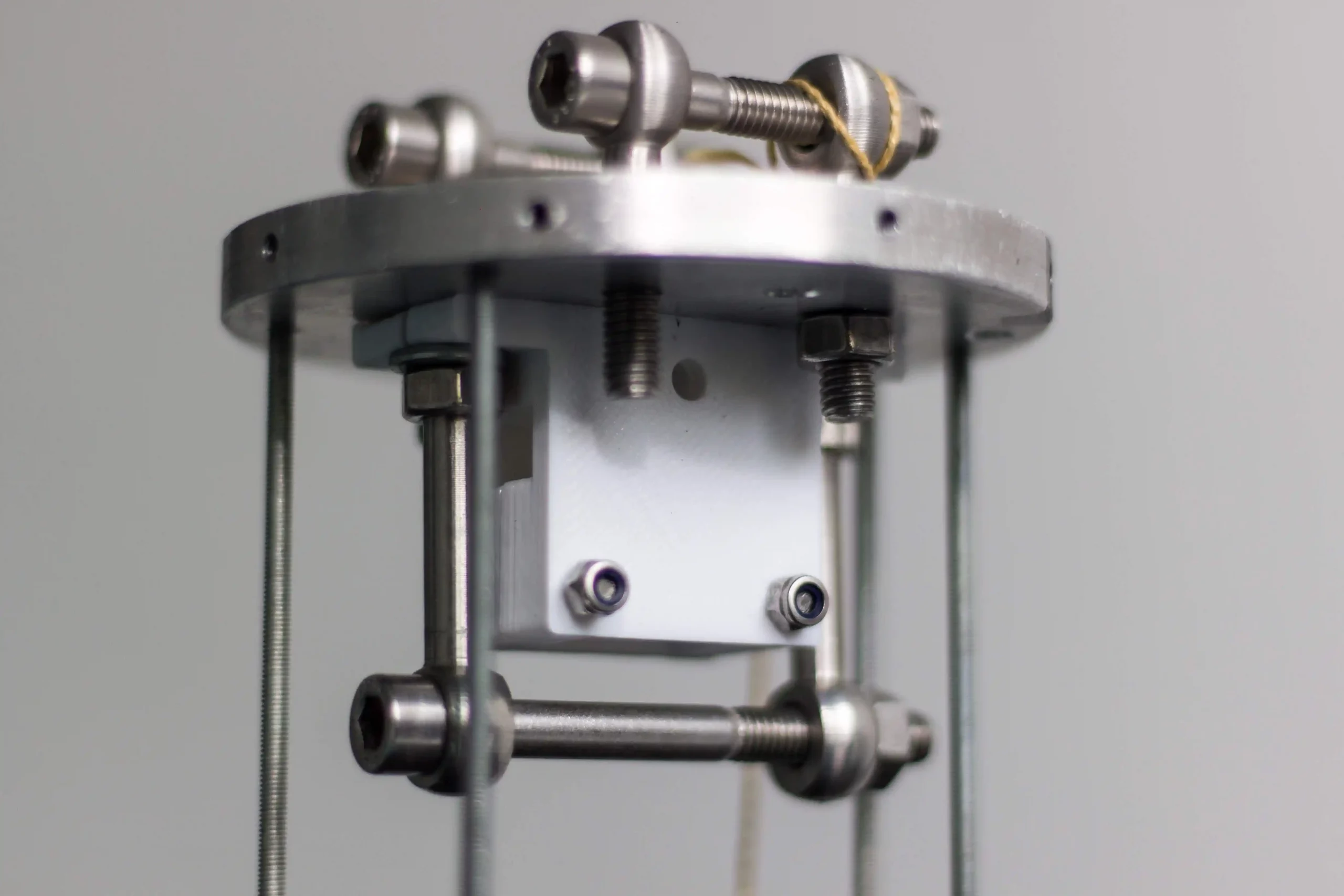
Expulsion
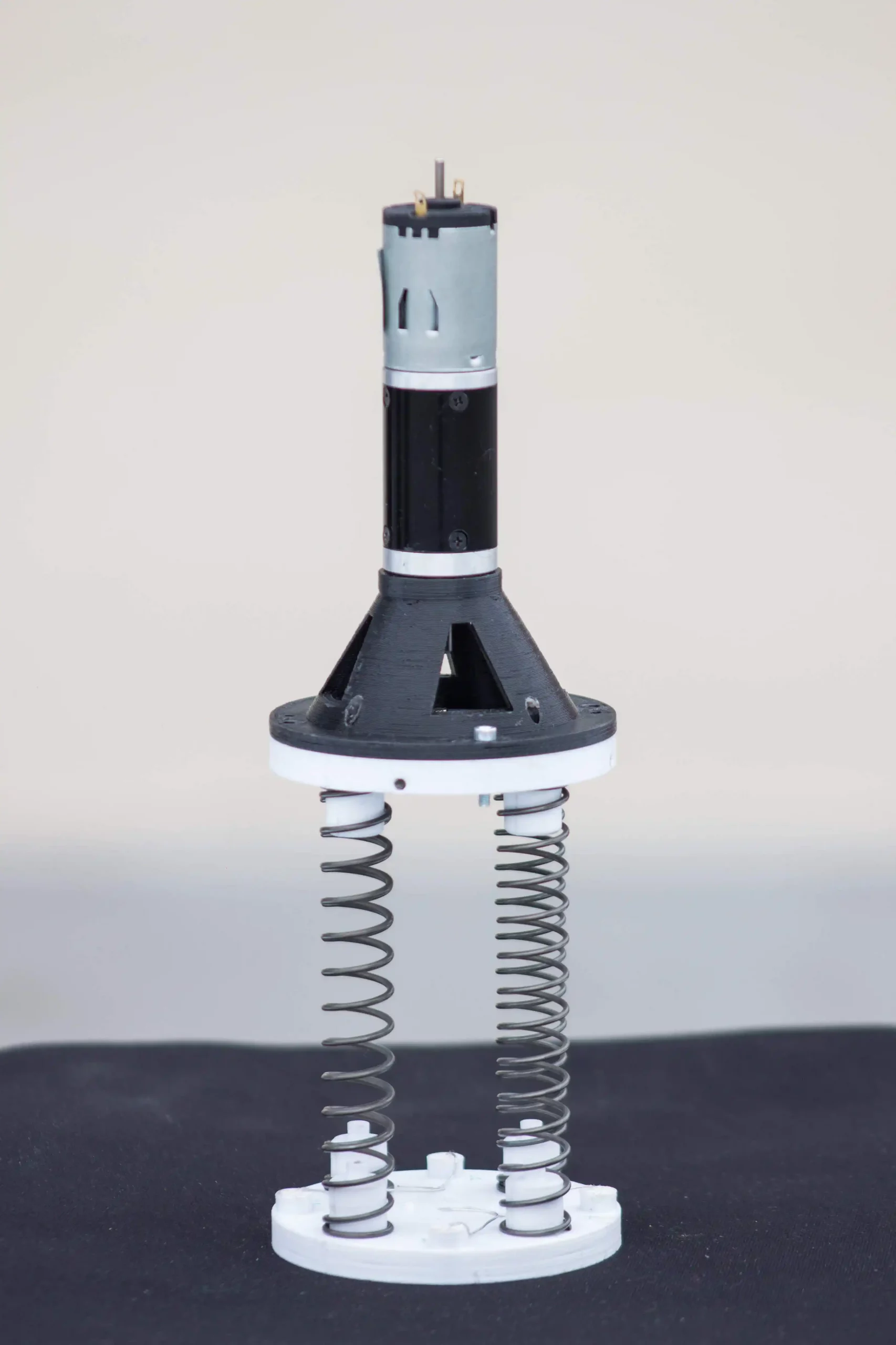
The expulsion mechanism is 3D printed and actuated by a DC motor that releases the energy stored in a 4 spring system. The motor unscrew a threaded M3 bar that connects the 2 parts and they come apart and the upper part connected with the nose cone is pushed forward and extract the part below and the drogue chute.
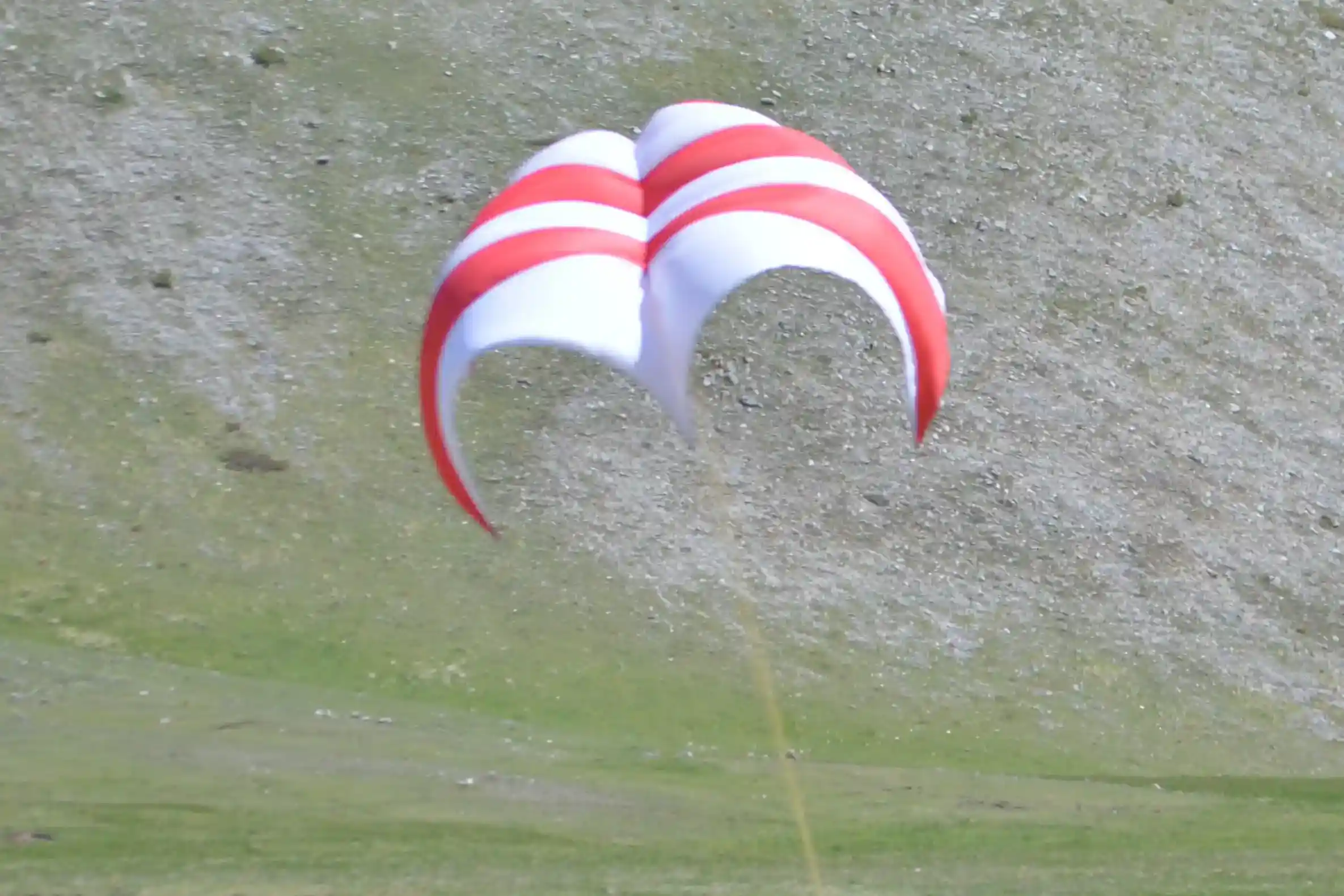
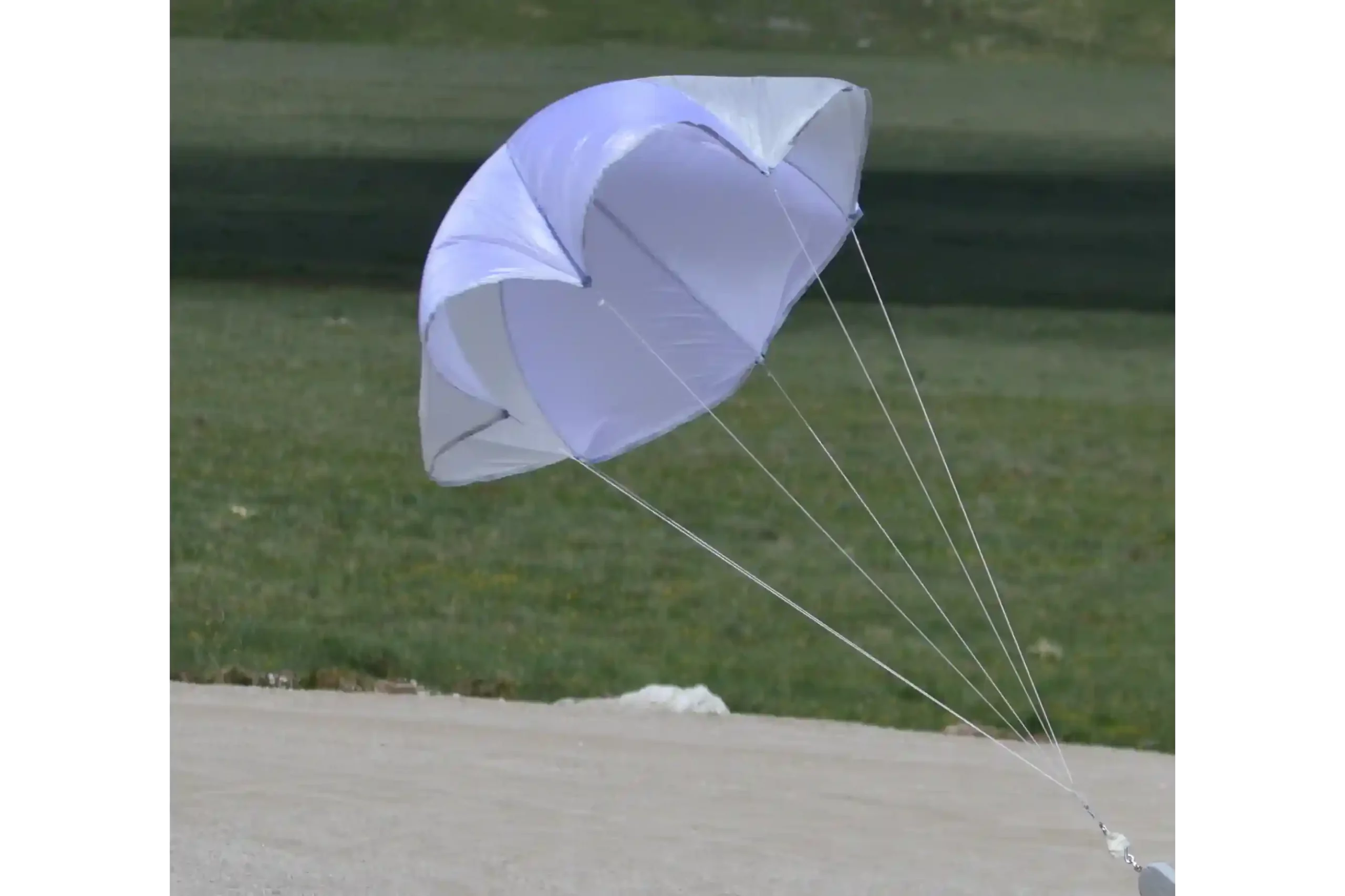
Recovery
The recovery system is composed by one drogue chute opened at apogee and then a controlled rogallo wing. The rogallo is actuated by three electric servo motors inserted in the fuselage controlled by the on-board computer to guide the rocket back home thanks to the wing. The staging of the 2 parachutes is performed by a Ni-Cr wire cutter that cuts the shock cords of the drogue by heating up and extracts the deployment bag of the main parachute (rogallo ndr).



